MSP430 Project 2
Make use of Pulse Width Modulation.
What is Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)?
This references the rate of ON vs OFF of a square wave. This is done to simulate voltage level with a digital signal using a transistor/MOSFET.
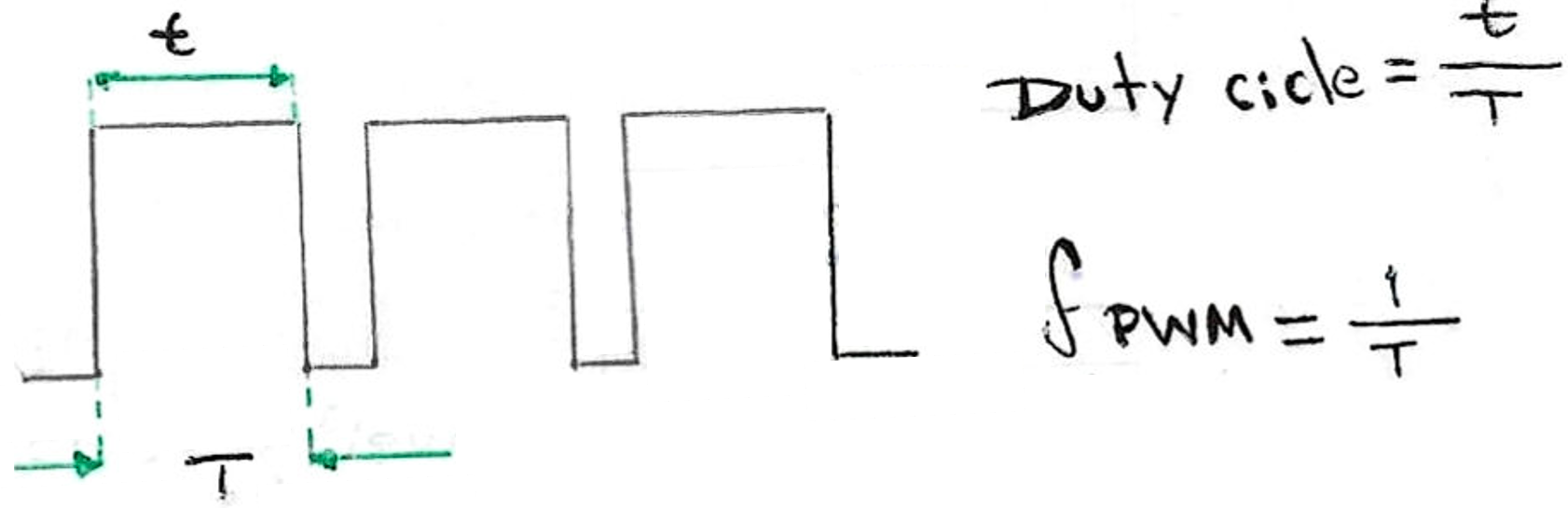
The PWM module of the microcontroller creates a square wave using a particular frequency (typically a high, like 10kHz). Then, we can change the duty cycle (% of ON state) of the signal:
From the MSP430G2xx datasheet:
Timer_A is a 16-bit timer counter with three capture compare registers. Timer_A can support multiple capture compares, PWM outputs, and interval timing. Timer_A also has extensive interrupt capabilities. Interrupts may be generated from the counter on overflow conditions and from each of the capture compare registers.
Timer_A features include:
-Configurable outputs with PWM capability
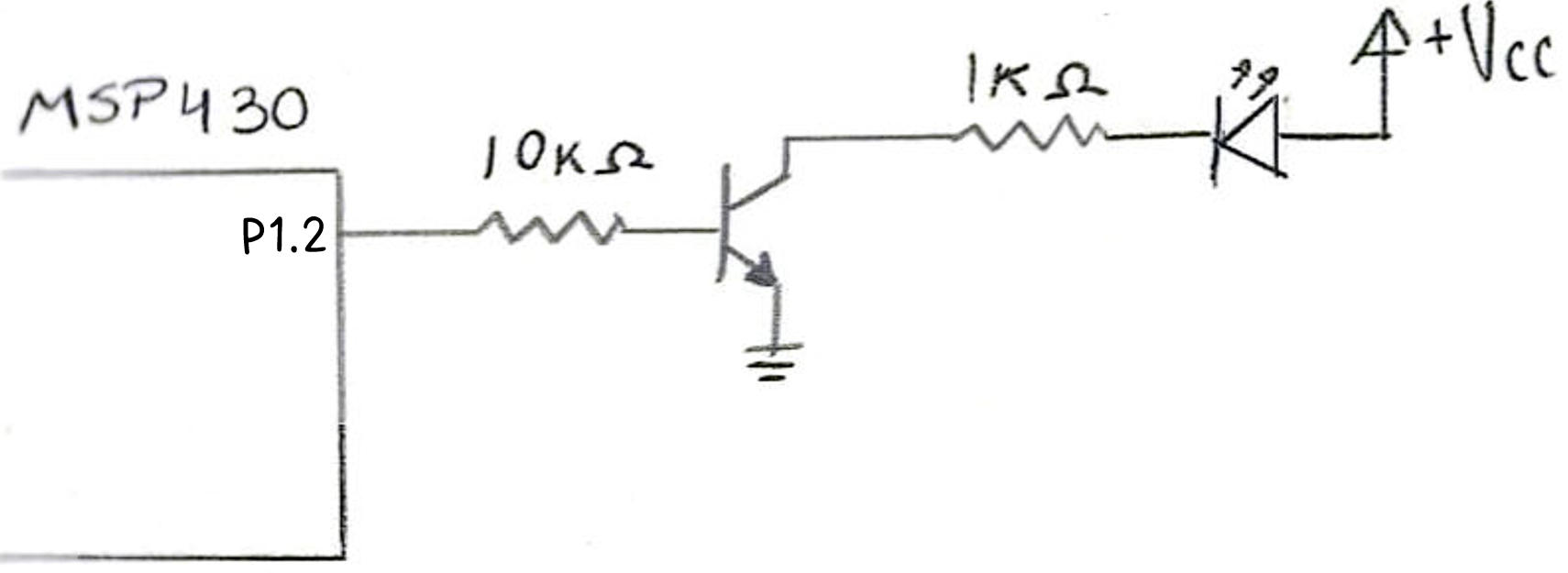
Now, we'll use a single LED and a transistor to give it enough current. Given that this PWM is at 50% duty cycle, the LED should be at MEDIUM brightness.
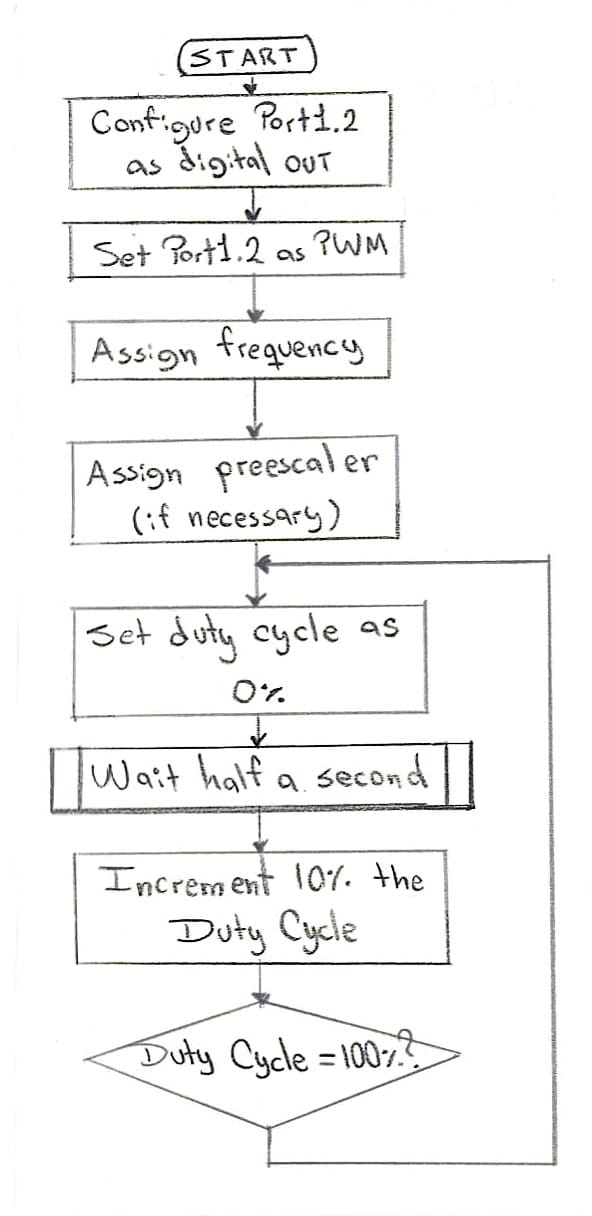
The proposed program will start from 0% brightness (or 0% Duty Cycle), increment 1% duty cycle each 0.1 seconds until it reaches 100% brightness; then it will reset to 0% brightness and wait one second before starting this pattern again.
#include "msp430g2452.h"
#include <msp430.h>
void configureClocks();
void delay_ms(unsigned int ms);
void delay_us(unsigned int us);
void configureClocks(){
WDTCTL = WDTPW + WDTHOLD; // Stop watchdog timer
BCSCTL1 = CALBC1_1MHZ; // Configure Clock to 1MHz
DCOCTL = CALDCO_1MHZ;
}
void delay_us(unsigned int us){
while (us){
__delay_cycles(1); // 1 for 1 Mhz set 16 for 16 MHz
us--;
}
}
void delay_ms(unsigned int ms){
while (ms){
__delay_cycles(1000); // 1000 for 1MHz and 16000 for 16MHz
ms--;
}
}
int main(void) {
configureClocks();
volatile short DutyCycle = 0;
// Configuring Port
P1DIR |= BIT2; // Set pin 1.2 to the output direction.
P1SEL |= BIT2; // Select pin 1.2 as our PWM output.
// Configuring timer for PWM
TA0CCR0 = 1000; //Set the period in the Timer A0 Capture/Compare 0 register to 1000 us.
TA0CCTL1 = OUTMOD_7;
TA0CCR1 = 0; //The period in microseconds that the power is ON. To obtain the Duty Cycle, divide this value over 1000, i.e. 500/1000 = 50% Duty Cycle.
TA0CTL = TASSEL_2 + MC_1; //TASSEL_2 selects SMCLK as the clock source, and MC_1 tells it to count up to the value in TA0CCR0.
while(1){
delay_ms(100); // Delay of 0.1 seconds
if(DutyCycle >= 100){ // Reset Duty Cycle and wait a second
DutyCycle = 0;
delay_ms(1000);
}
TA0CCR1 = DutyCycle * 10; // Multiplied by 10 so we can use a unitary Duty Cycle
DutyCycle += 1; // Increment 1%
}
}