ps
ps gives a snapshot of processes. Sot it is static and does not update unless it's called again.
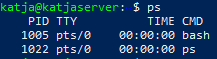
| Column -- | PID | TTY | TIME | CMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name -- | Process ID | TeleTYpewriter (Computer terminal) |
Executing time |
Executable name |
| Description -- | It is the unique identifier associated with that process. Multiple process from the same program have different PIDs. | It is the terminal that executed a particular commmand. | CPU utilization of process or thread, incremented each time the system clock ticks and the process or thread is found to be running. | It is the program that executed the command. |
A common way to use the ps command is with the -a flag to select all processes except both session leaders and processes not associated with a terminal, the u flag to select by effective user ID (EUID) or name; selecting only the processes belonging to a username present in userlist and the x flag to select any of the users.
ps -aux
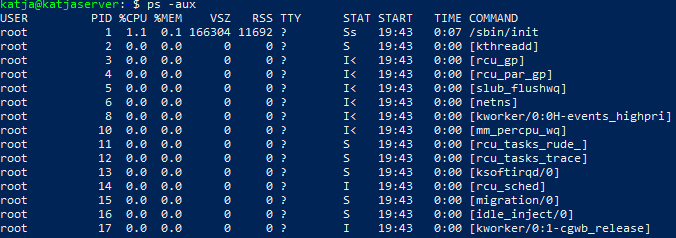
| Column -- | %CPU | %MEM | VSZ | RSS | STAT | COMMAND |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name -- | CPU utilization of the process. | Memory usage (RES). | Total VM size in KiB. | Resident Set Size | Muti-character process state. | Name of the process |
| Description -- | How much of the CPU the process is using. It is the CPU time used divided by the time the process has been running (cputime/realtime ratio). |
How much Memory the process is using. A task's currently used share of the available physical memory. Ratio of the process's resident set size to the physical memory on the machine, expressed as a percentage. |
Virtual memory size of the process in KiB. | The non-swapped physical memory that a task has used (in kibibytes). | See Process State Codes | A command with all its arguments as a string. |