Processors
In computers, the Central Processing Unit (CPU) processes electrical signals; treated as having one of the binary values 1 or 0.
CPU architecture is a reference to the instructions that the processor supports. Although Intel and AMD make processors supporting the same instructions it is meaningful to differentiate by vendor because of vendor specific packaging, performance, and power consumption differences.
Software distributions commonly use these designations to specify the minimum set of instructions they require to operate:
| CPU Architecture | Description |
|---|---|
i386 |
References the 32-bit instruction set associated with the Intel 80386 |
x86 |
Typically references the 32-bit instruction sets associated with successors to the 80386 such as 80486, 80586, and Pentium |
x64 / x86-64 |
References processors that support both the 32-bit and 64-bit instructions of the x86 family. |
AMD |
A reference to x86 support by AMD processors. |
AMD64 |
A reference to x64 support by AMD processors. |
ARM |
References a Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) CPU that is not based on the x86 instruction set. Commonly used by embedded, mobile, tablet, and battery operated devices. A version of Linux for ARM is used by the Raspberry Pi. |
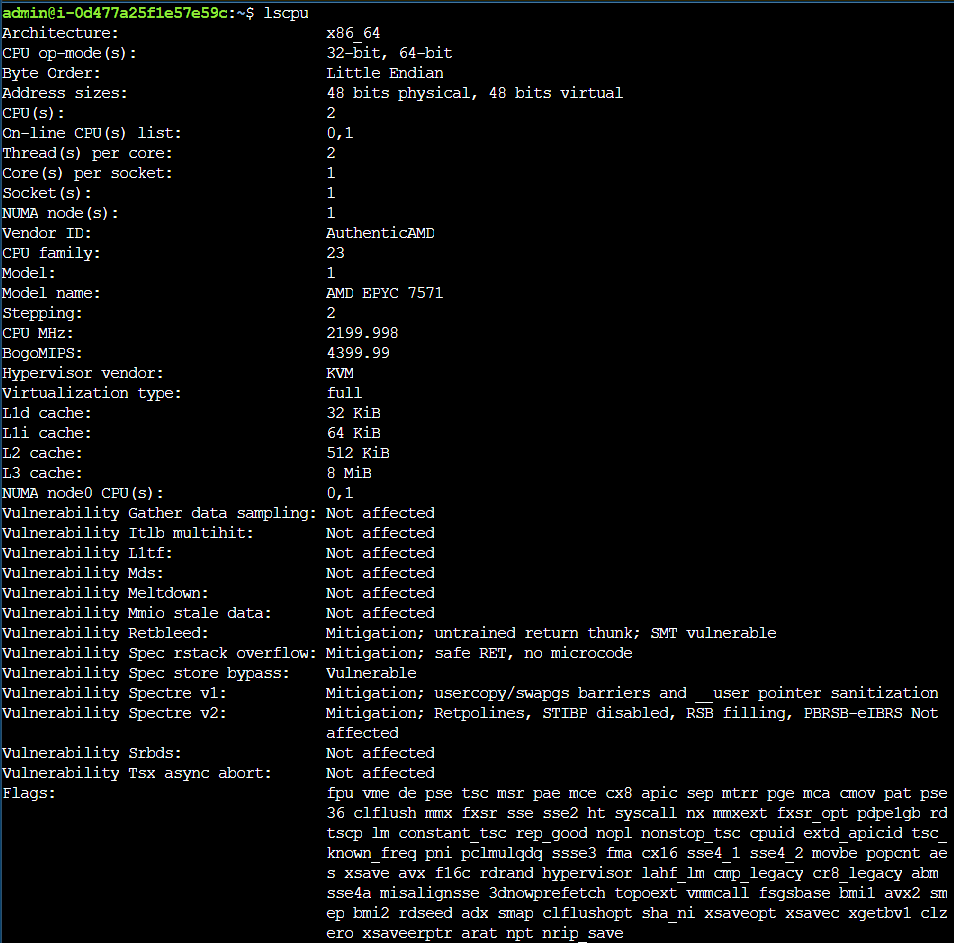
The file /proc/cpuinfo contains detailed information about a system's processor.
A more general result can be obtained with the command lscpu.