C++ classes encapsulate data and associated functionality into an object:
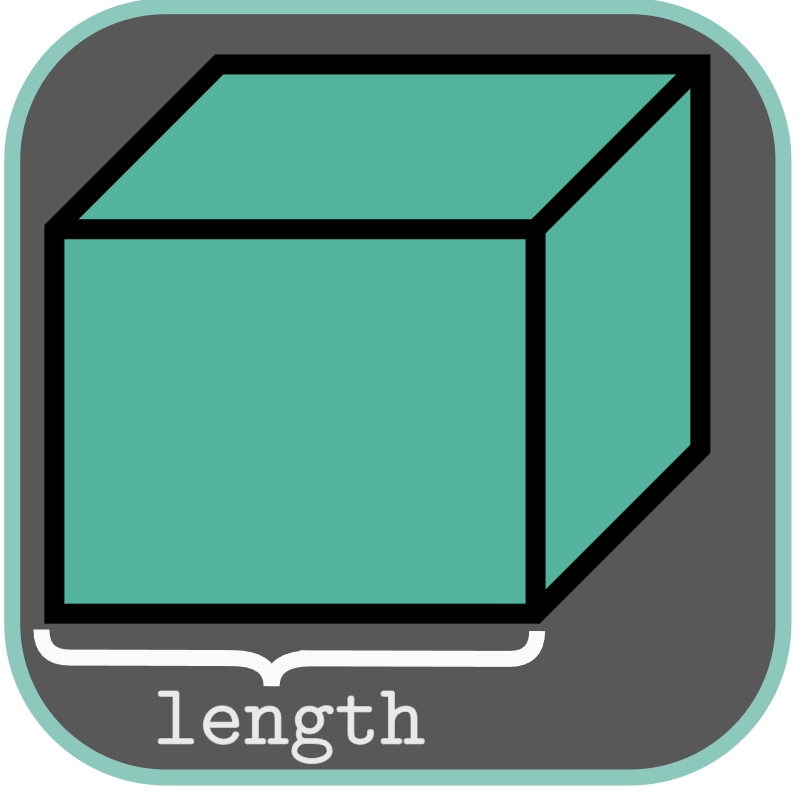
class Cube {
public:
double getVolume();
// ...
private:
double length_;
};
Encapsulation encloses data and functionality into a single unit (called a class):
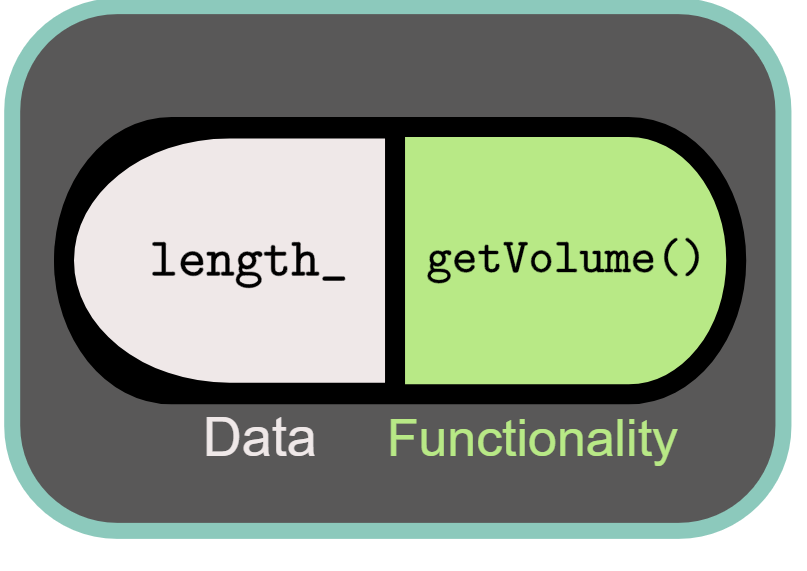
In C++, data and functionality are separated into two separate protections: public and private.
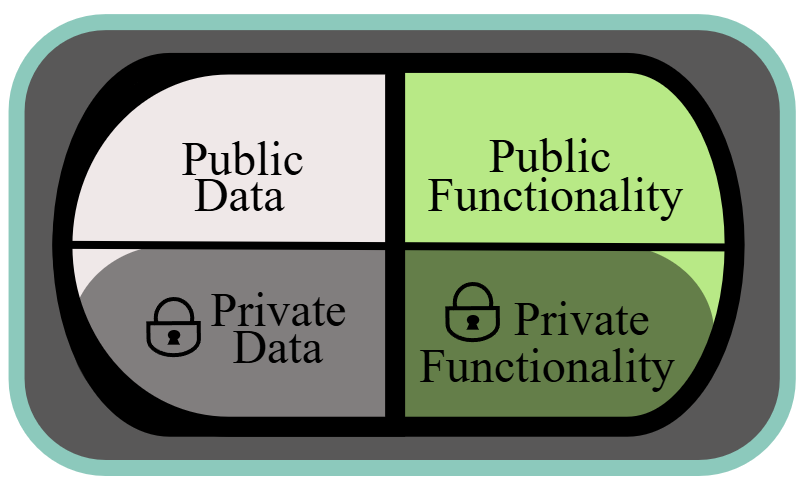
Public vs Private
The protection level determines the access that "client code" has to the member data or functionality:
- Public members can be accesses by client code.
- Private members cannot be accessed by client code (only used within the class itself).
Encapsulation # 2
In C++, the interface (.h file) to the class is defined separately from the implementation (.cpp file).

