Pointer operations
Read operation on a pointer
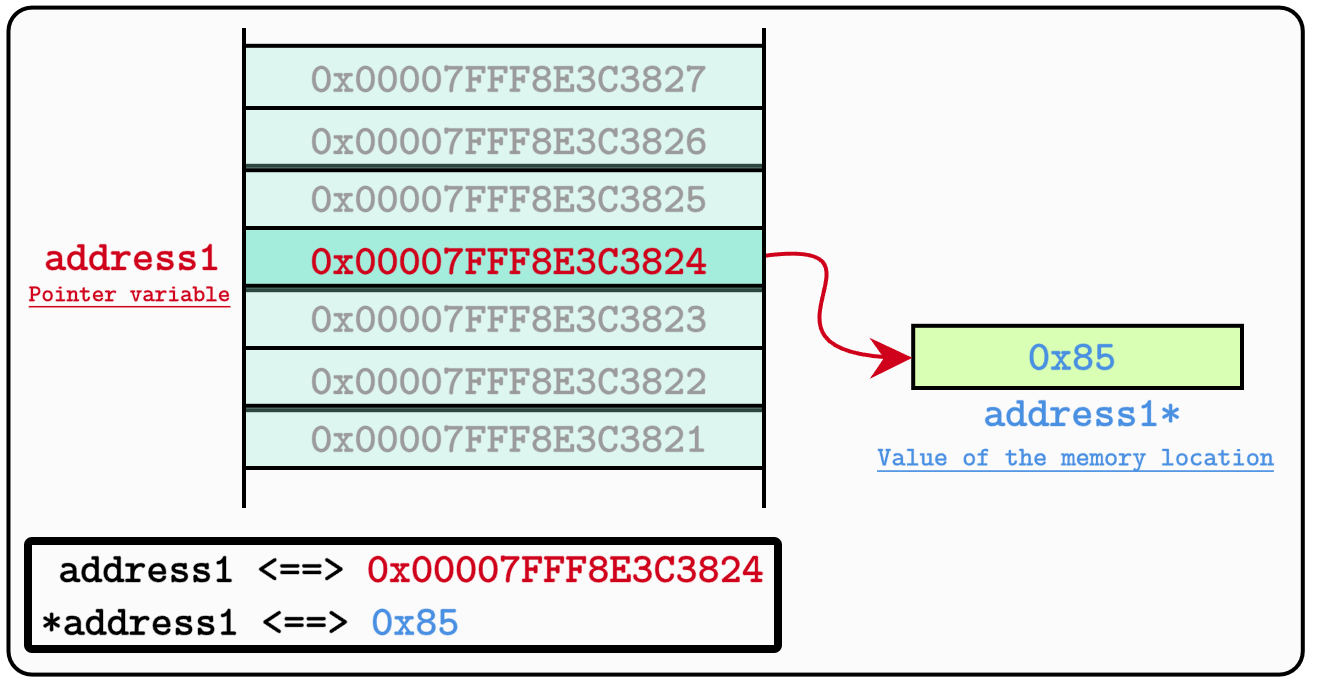
Given a pointer:
char* address1 = (char*) 0x00007FFF8E3C3824;
to read the data stored in that address, we need to dereference it, like this:
char data = *address1; // Dereferencing a pointer to read data
With the result being that 1 byte of data is read from the pointer and stored into the data variable.
Important
* is the "Value at address" operator
& is the "Address of" operator
Write operation on a pointer
To write data to a pointer the address must be dereferenced
*address1 = 0x89; // Dereferencing a pointer to write data
This assigns the value 0x89 to the address being pointed at.
Example:
#include <iostream>
int main(){
// Create an int type variable and initialize it to value 100
int variable1 = 100;
// Print the address of the above variable
std::cout<<"Address of variable1 = "<<&variable1<<std::endl;
// Create a pointer variable and store the address of the above variable
int* variable1_ptr = &variable1;
// Perform read operation on the pointer variable to fetch 1 byte of data from the pointer
int read_variable1 = *variable1_ptr;
// Print the data obtained from the read operation on the pointer.
std::cout<<"Fetch 1 byte of data = "<<read_variable1<<std::endl;
// Perform write operation on the pointer to store the value 65
*variable1_ptr = 65;
// Print the value of the variable defined in step 1
std::cout<<"Value of variable = "<<*variable1_ptr<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Address of variable1 = 0x7ffd2ac75208
Fetch 1 byte of data = 100
Value of variable = 65