Scaling Amazon EC2
Scalability
Involves beginning with only the resources you need and designing your architecture to automatically respond to changing demand by scaling out or in.
Pay only the resources you use with Amazon Auto Scaling
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling enables you to automatically add or remove Amazon EC2 instances in response to changing application demand.
Within Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, you can use two approaches: dynamic scaling and predictive scaling.
- Dynamic scaling responds to changing demand.
- Predictive scaling automatically schedules the right number of Amazon EC2 instances based on predicted demand.
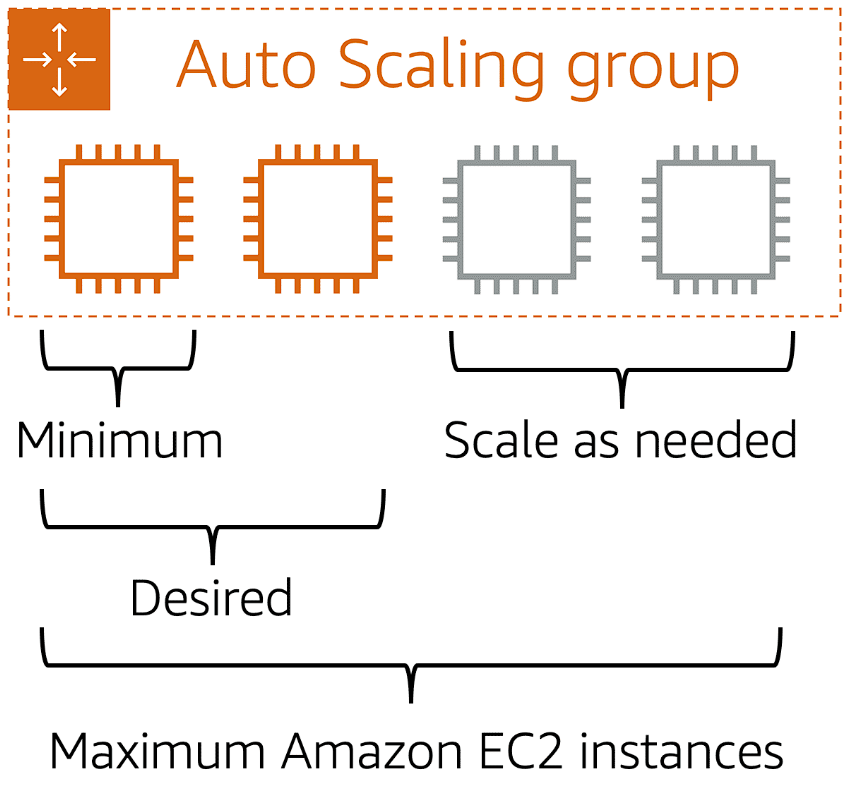
When you create an Auto Scaling group, you can set the minimum number of Amazon EC2 instances. The minimum capacity is the number of Amazon EC2 instances that launch immediately after you have created the Auto Scaling group. In this example, the Auto Scaling group has a minimum capacity of one Amazon EC2 instance.
Next, you can set the desired capacity at two Amazon EC2 instances even though your application needs a minimum of a single Amazon EC2 instance to run.
The third configuration that you can set in an Auto Scaling group is the maximum capacity. For example, you might configure the Auto Scaling group to scale out in response to increased demand, but only to a maximum of four Amazon EC2 instances