Additional Compute Services
If you have applications that you want to run in Amazon EC2, you must do the following:
- Provision instances (virtual servers).
- Upload your code.
- Continue to manage the instances while your application is running.
The term “serverless” means that your code runs on servers, but you do not need to provision or manage these servers. With serverless computing, you can focus more on innovating new products and features instead of maintaining servers.

AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service that allows you to run code in response to events without managing services.
It enables us to write functions that are triggered by specific events, such as HTTP Requests, changes in a database, or incoming data from services.
Lambda automatically scales in response to the volume of requests, meaning you only pay for the compute time you use, making it cost-effective and efficient.
-
Event driven: Lambda functions are triggered by events. For example, in an IoT application, an HTTP POST request containing sensor data can trigger a Lambda function to process that data.
-
Function as a Service: Each Lambda function contains the code and configuration required to perform a specific task, like storing data in a database or sending alerts.
-
Automatic Scaling: Lambda automatically scales up to handle increased loads and scales down to zero when no requests are present, making it ideal for fluctuating workloads.
-
Pay-as-You-Go Pricing: Pay only the time you use.
Benefits of using AWS Lambda in IoT Applications
- Scalability: Lambda can handle high volumes of data, scaling up or down as necessary.
- Cost Efficiency: Ideal for IoT applications where data processing is periodic or event-driven.
- Low Maintenance: As a fully managed service, AWS Lambda reduces operation overhead.
- Easy Integration: Lambda integrates with various AWS services like API Gateway, DynamoDB, and IoT Core, creating a seamless IoT data pipeline.
Key Components of an AWS Lambda Function
- Function Code: The code to perform a specific action, such as processing sensor data. Lambda supports several programming languages, including Python, Node.js, and Java, making it versatile for different types of projects.
- Event Source: Lambda functions are event-driven, meaning they're triggered by an event source. Common event sources include API Gateway for HTTP Requests, S3 for file uploads, and DynamoDB or IoT Core for data streaming.
- Environment Variables: Lambda functions can use environment variables for configuration, such as API keys, database connection strings, or other sensitive information.
- Execution Role: Lambda functions run with permissions granted by an AWS IAM Role. This role determines what the Lambda function can access (e.g. DynamoDB tables, S3 buckets) and ensures security by limiting permissions.
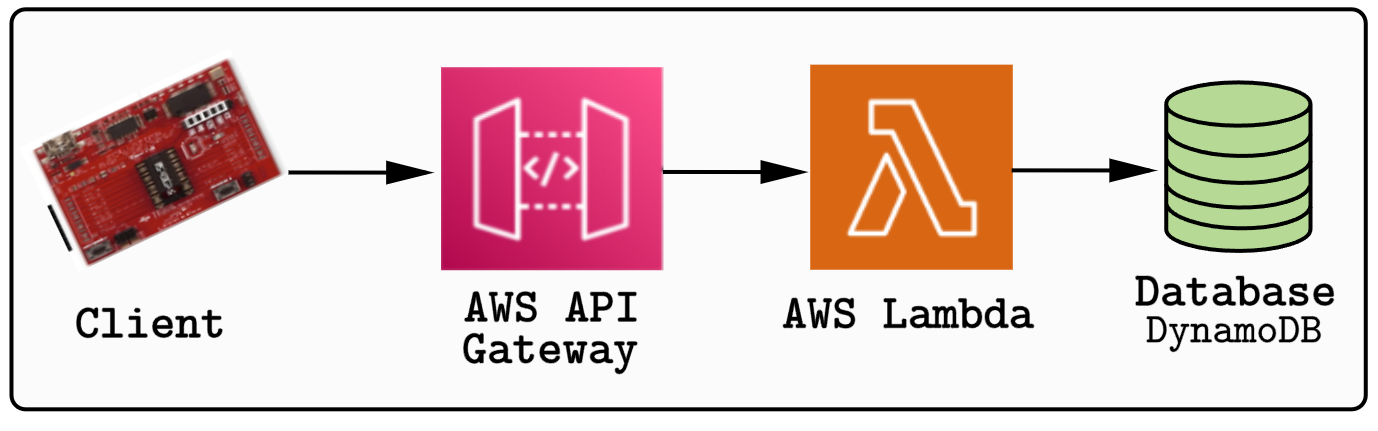
- In our IoT system, AWS Lambda functions serve as the main processor of incoming data from IoT devices, such as temperature or humidity readings.
- A Lambda function can be triggered by API Gateway when a device sends an HTTP POST request with sensor data. The function can:
- Parse the JSON payload from the request.
- Extract the sensor data (e.g., temperature, humidity, timestamp).
- Store the data in DynamoDB for long-term storage and analysis.
Another Lambda function can retrieve data when an HTTP GET request is made (e.g. /data/latest).
This function queries DynamoDB for the latest record associated with a device.